WHOLE GENOME RESEQUENING

Genomics monitoring of SARS-CoV-2 uncovers an Nsp1 deletion variant that modulates type I interferon response
Nanopore | Illumina | Whole genome resequencing | metagenomics | RNA-Seq | Sanger
Biomarker Technologies provided technical support on sample sequencing in this study.
Highlights
1.SARS-CoV-2 genome sequencing and phylognetic analysis identify 35 recurrent mutations including 31 SNPs and 4 Indels.
2.Association with 117 clinical phenotypes reveals potentially
important mutations.
∆500-532 in Nsp1 coding region correlates with lower viral
3.load and serum IFN-β.
4.Viral isolates with ∆500-532 mutation induce lower IFN-I
response in the infected cells.
Experimental Design
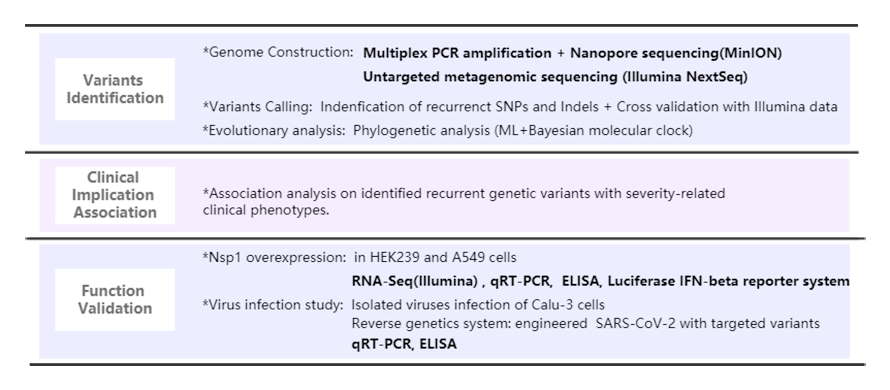
Achievements
1. COVID-19 epidemiological and genomic surveillance
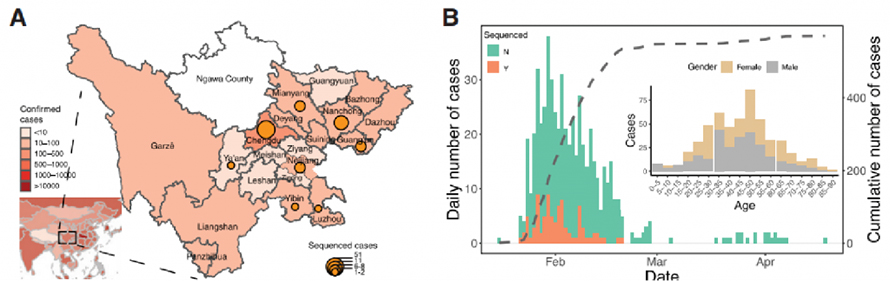
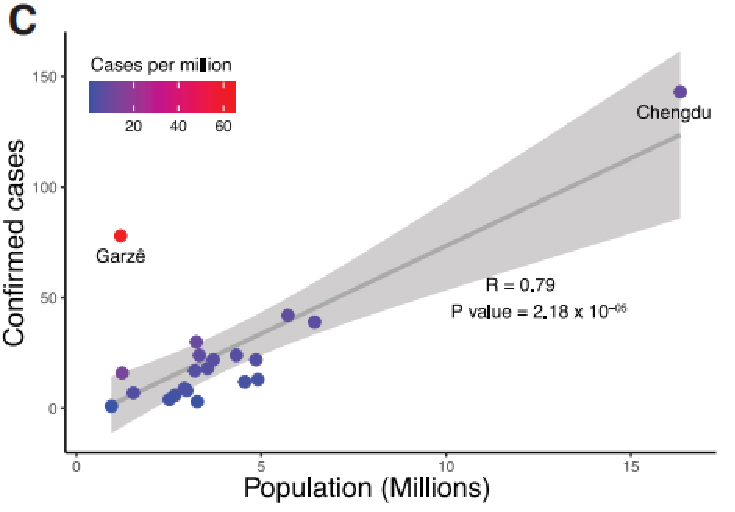
Clinical data was collected in Sichuan province, China across the outbreak period from Jan. 22nd, 2020 to Feb. 20th, 2020. A total of 538 COVID-19 cases were confirmed by qPCR tests in Sichuan, 28.8% of which were from the province capital. Confirmed cases in Sichuan increased exponentially, peaking on Jan. 30th. Also, data supported that social distancing can be a key factor in preventing virus spread.
Figure 1. Epidemiological study of COVID-19 in Sichuan province, China
2. SARS-CoV-2 genome construction and variants identification
With multiplex PCR amplification followed by nanopore sequencing, a total of 310 near- or partial-complete genomes from 248 patients were generated with approx. 80% of genomes covered by 10 reads(Mean depth: 0.39 M reads per sample).
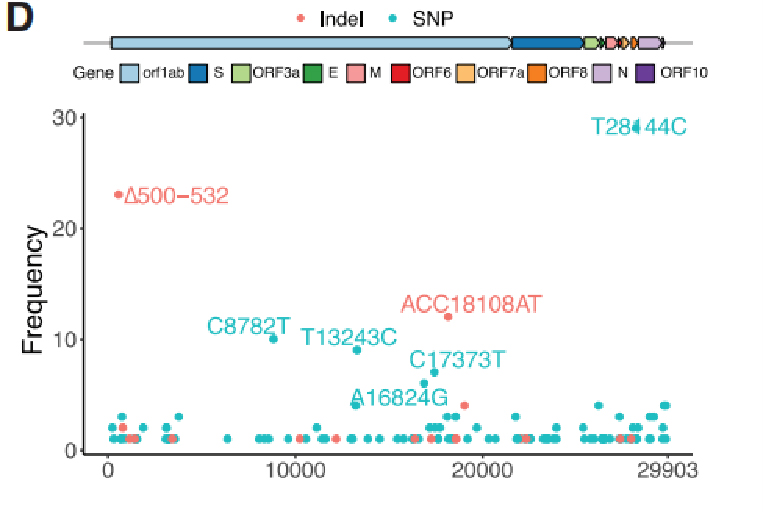
Figure 2. Frequency of each variants in the Sichuan cohort
A total of 104 SNPs and 18 Indels were identified from SARS-CoV-2 genomes, in which 31 SNPs and 4 Indels were identified as recurrent genetic variants. By comparing them with 169 samples from Wuhan and with 81,391 high-quality publich genome sequences in GISAID, 29 of the 35 variants found presented in other continents. Notably, four variants including ∆500-532, ACC18108AT, ∆729-737 and T13243C, were only found to present in Sichuan and Wuhan and absent in GISAID data, indicating that these variants were very likely to be improted from Wuhan, which meet the travel records of patients.
Evolutionary analysis with maximum likelihood(ML) method and Bayesian molecular clock approaches was processed on 88 new virus sfrom Sichuan and 250 curated genomes from other regions. Genomes with ∆500-532 (Deletions in Nsp1 coding region) were found distributed sparsely in the phylogenetic tree. Haplotype analysis on Nsp1 variants identified 5 of them from multiple cities. These results suggested that the ∆500-532 occurred in multiple cities and might be imported multiple times from Wuhan.
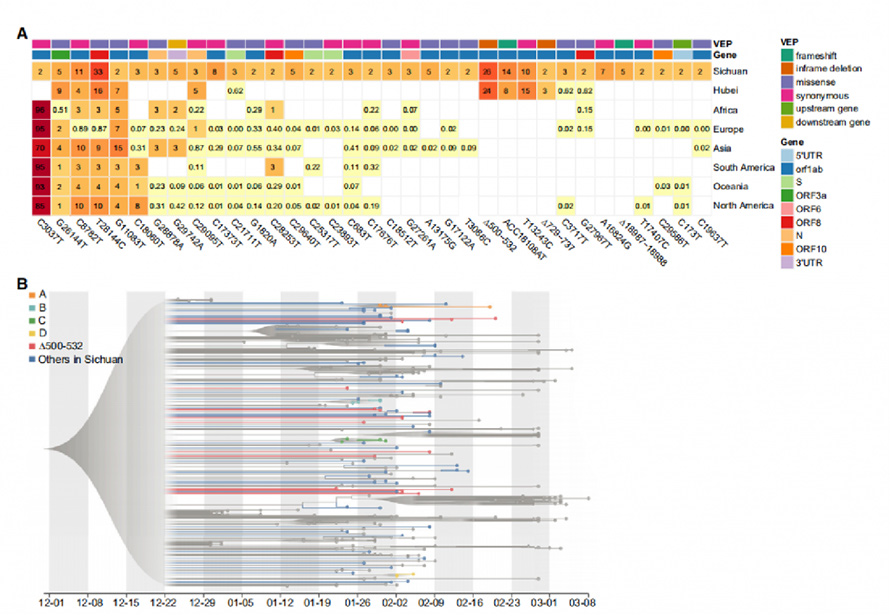
Figure 2. Recurrent genetic variants and phylogenetic analysis in the SARS-CoV-2 genomes
3. Association of recurrent genetic variants with clinical implications
117 clinical phenotypes were associated with COVID-19 severity, where 19 severity-related phenotypes were classified into severe and non-severe traits. Relationship between these traits and 35 recurrent genetic variants were viualized in bi-cluster heatmap. A GSEA-like ranked enrichment analysis shown that ∆500-532 is negatively correlated with ESR, serum IFN-β andCD3+CD8+ T cell counts in the blood. Moreover,qPCR tests shown that patients infected with virus harboring ∆500-532 had the highest Ct value, i.e. lowest viral load.
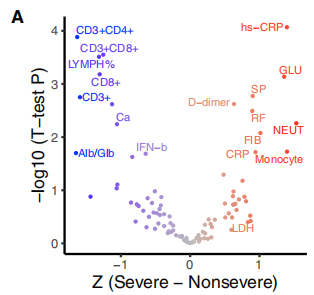
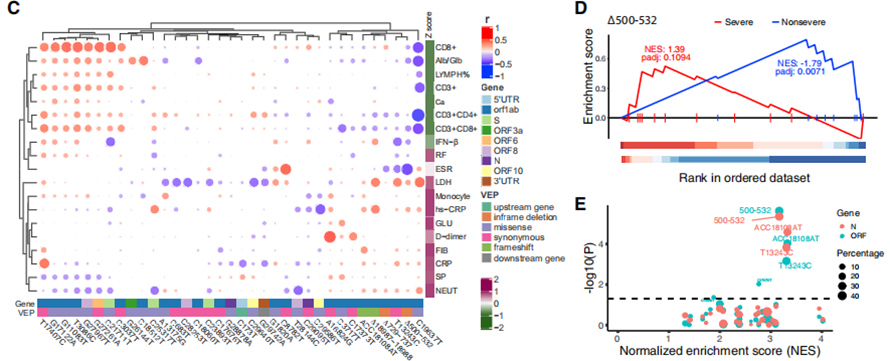
Figure 3. Associations of 35 recurrent genetic variants with clinical phenotypes
4. Validation on viral mutation associated clinical phenotypes
In order to understand the affects of ∆500-532 on Nsp1 functions, HEK239T cells were transfected with plasmids expressing full-length, WT Nsp1 and mutant forms with deletions. Transcriptome profiles of each treated HEK239T cells were processed for PCA analysis, showing that deletion mutants clustered relatively closer and were significantly different from WT Nsp1. The genes that were significantly upregulated in the mutants were mainly enriched in “peptide biosynthetic/metabolic process”, “ribonucleoprotein complex biogenesis”, “protein targeting to membrane/ER”, etc. Moreover, two deletions showed a distinct expssion pattern from WT.
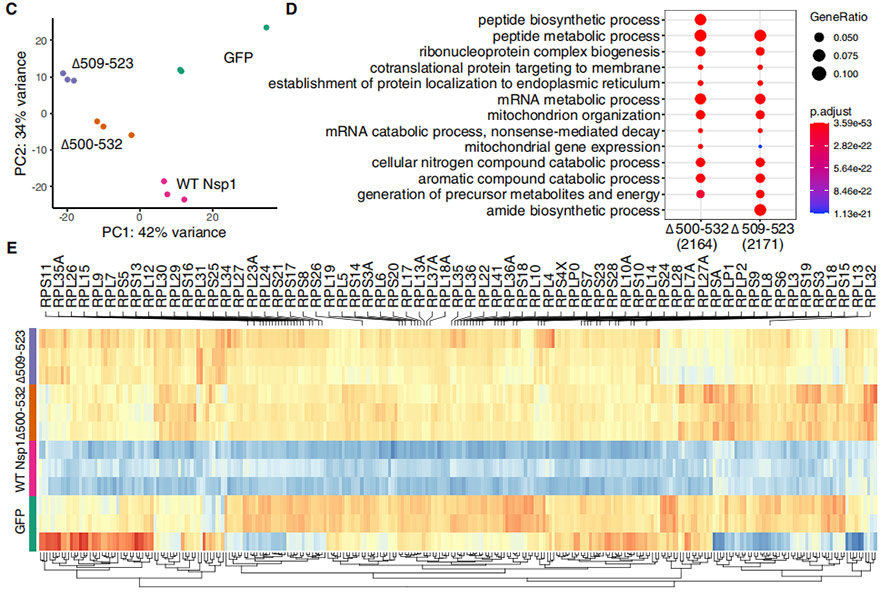
Figure 4. Transcriptome analysis on HEK239T cells transfected by WT Nsp1 and that with deletions
The affects of deletions on IFN-1 response was also tested in overexpressed study. All tested deletions were shown to reduce IFN-1 repsonse in transfected HEK239T and A549 cells at both transcriptome level and protein level. Interestingly, the significantly down-regulated genes in deletions were enriched in “defense response to virus”, “viral genome replication”, “regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II” and “response to type I interferon”.
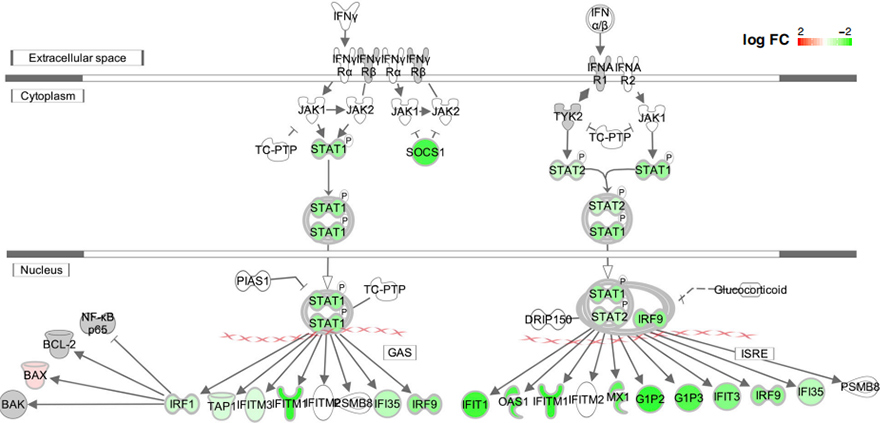
Figure 5. Down regulation of interferon signaling pathways in ∆500-532 mutant
In this study, the impact of these deletions on virus were further confirmed by viral infection studies. Viruses with certain mutants were isolated from clinical samples and infected to Calu-3 cells. Detailed results on viral infection study can be read in the paper.
doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2021.01.015
Reference
Lin J, Tang C, Wei H, et al. Genomic monitoring of SARS-CoV-2 uncovers an Nsp1 deletion variant that modulates type I interferon response[J]. Cell host & microbe, 2021.
News and Highlights aims at sharing the latest successful cases with Biomarker Technologies, capturing novel scientific achievements as well as prominent techniques applied during the study.
Post time: Jan-06-2022

