Hi-C Based Genome Assembly
Service Features
● Sequencing on Illumina NovaSeq with PE150.
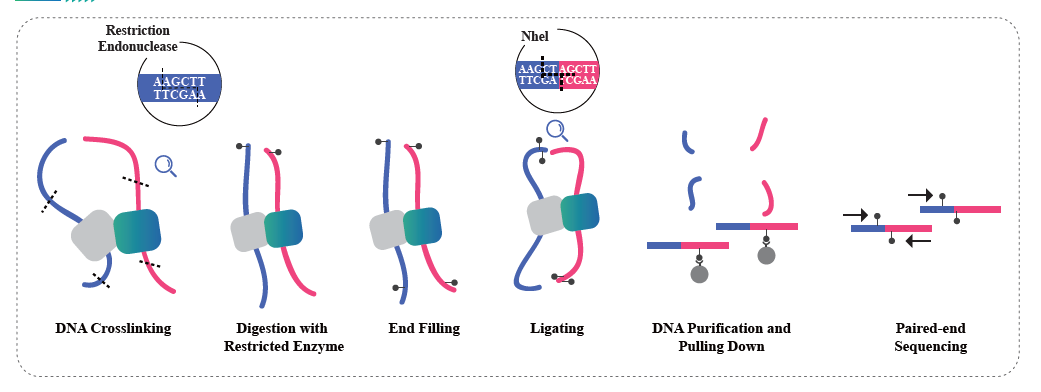
● Service requires tissue samples, instead of extracted nucleic acids, to cross-link with formaldehyde and conserve the DNA-protein interactions.
● The Hi-C experiment involves restriction and end repair of the sticky ends with biotin, followed by circularization of the resulting blunt ends while preserving the interactions. The DNA is then pulled down with streptavidin beads and purified for subsequent library preparation.
Service Advantages
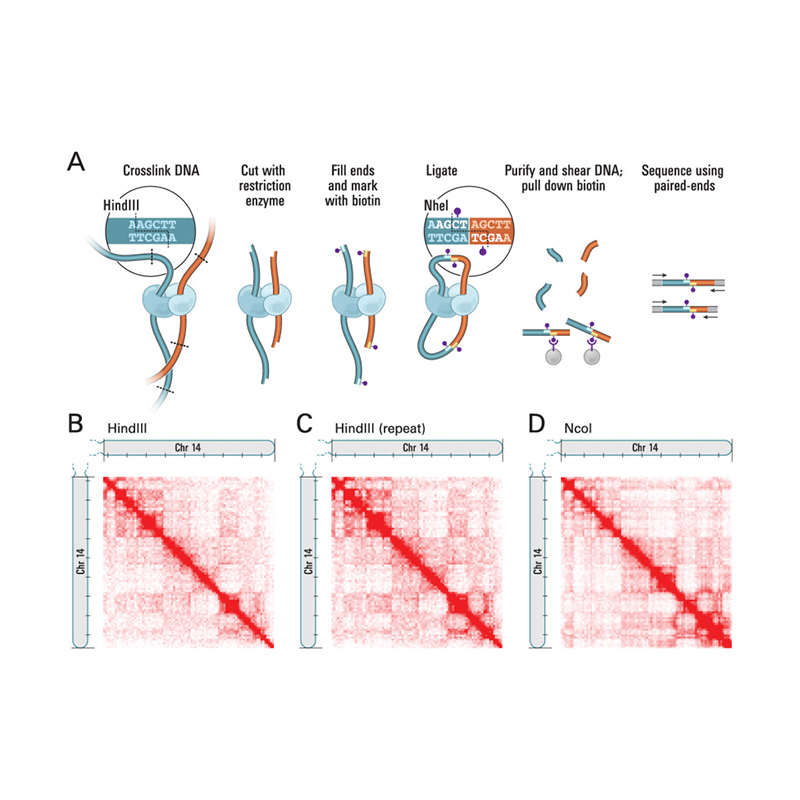
Overview of Hi-C
(Lieberman-Aiden E et al., Science, 2009)
● Eliminating the Need for Genetic Population Data: Hi-C substitutes the essential information required for contig anchoring.
● High marker density: leading to a high contig anchoring ratio above 90%.
● Extensive Expertise and publication records: BMKGene has vast experience with more than 2000 cases of Hi-C Genome Assembly from 800 different species and various patents. Over 100 published cases have an accumulative impact factor of over 900.
● Highly skilled bioinformatics team: with in-house patents and software copyrights for Hi-C experiments and data analysis, the self-developed visualization data software enables manual block moving, reversing, revoking, and redoing.
● Post-Sales Support: Our commitment extends beyond project completion with a 3-month after-sale service period. During this time, we offer project follow-up, troubleshooting assistance, and Q&A sessions to address any queries related to the results.
● Comprehensive Annotation: we use multiple databases to functionally annotate the genes with identified variations and perform the corresponding enrichment analysis, providing insights on multiple research projects.
Service Specifications
|
Library preparation |
Sequencing strategy |
Recommended data output |
Quality control |
|
Hi-C library |
Illumina NovaSeq PE150 |
100x |
Q30≥85% |
Sample Requirements
|
Tissue or extracted nucleic acids |
Required amount |
|
Animal Viscera |
≥2g |
|
Animal Muscle |
|
|
Mammalian Blood |
≥2mL |
|
Poultry/Fish Blood |
|
|
Plant- Fresh Leaf |
≥4g |
|
Cultured Cells |
≥1x107 |
Service Work Flow

Experiment design
Sample delivery
DNA extraction
Library construction
Sequencing

Data analysis
After-sale services
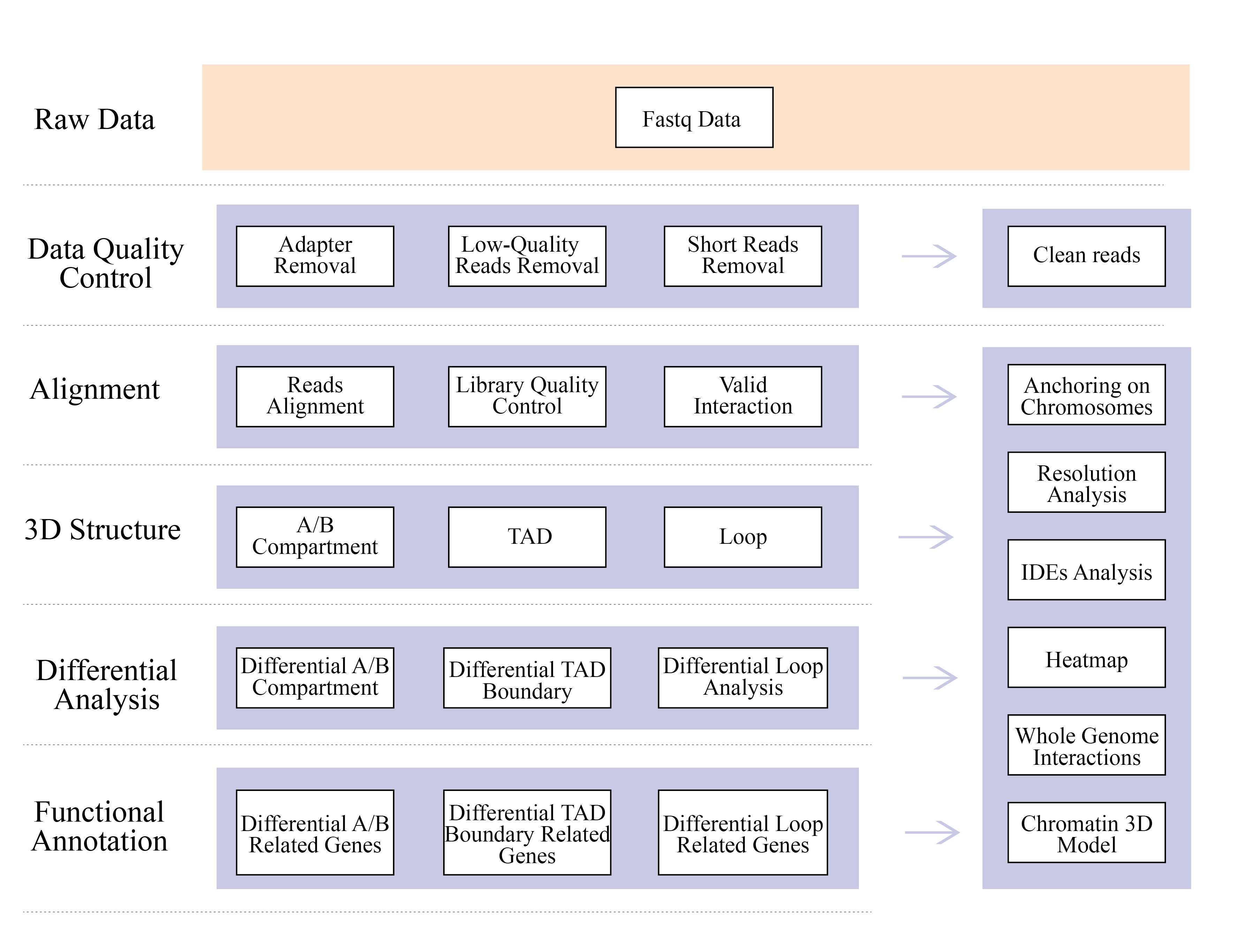
1) Raw data QC
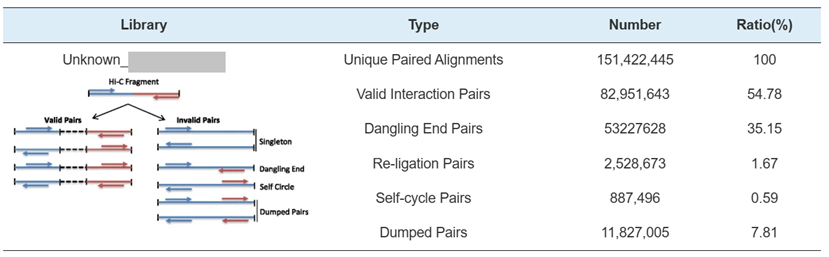
2) Hi-C library QC: estimation of valid Hi-C interactions
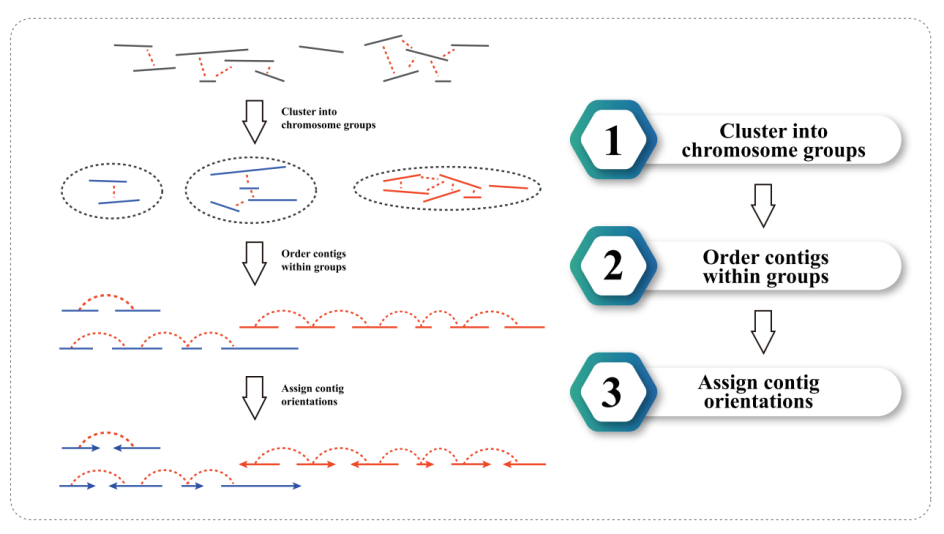
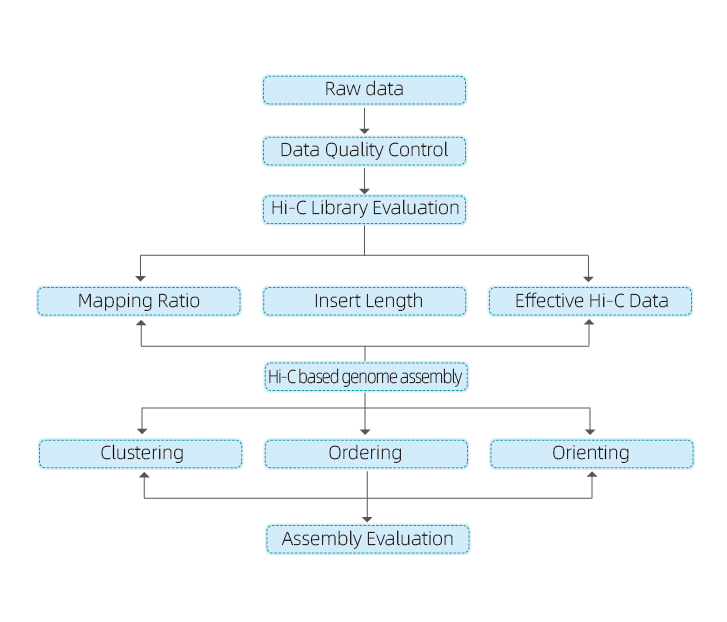
3) Hi-C assembly: clustering of contigs in groups, followed by contig ordering within each group and assigning contig orientation
4) Hi-C evaluation
Hi-C Library QC – estimation of Hi-C valid interaction pairs
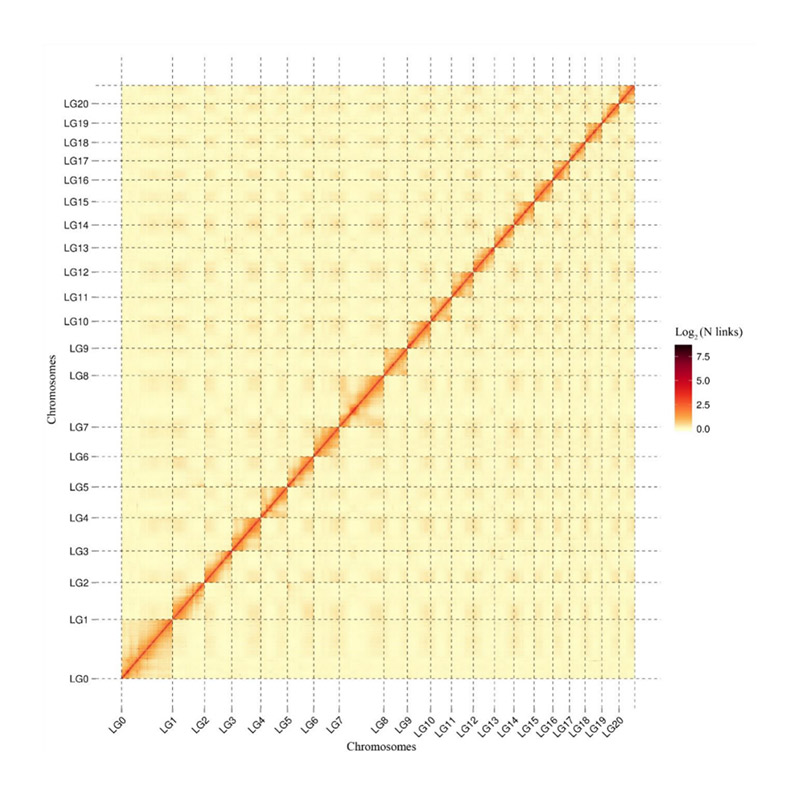
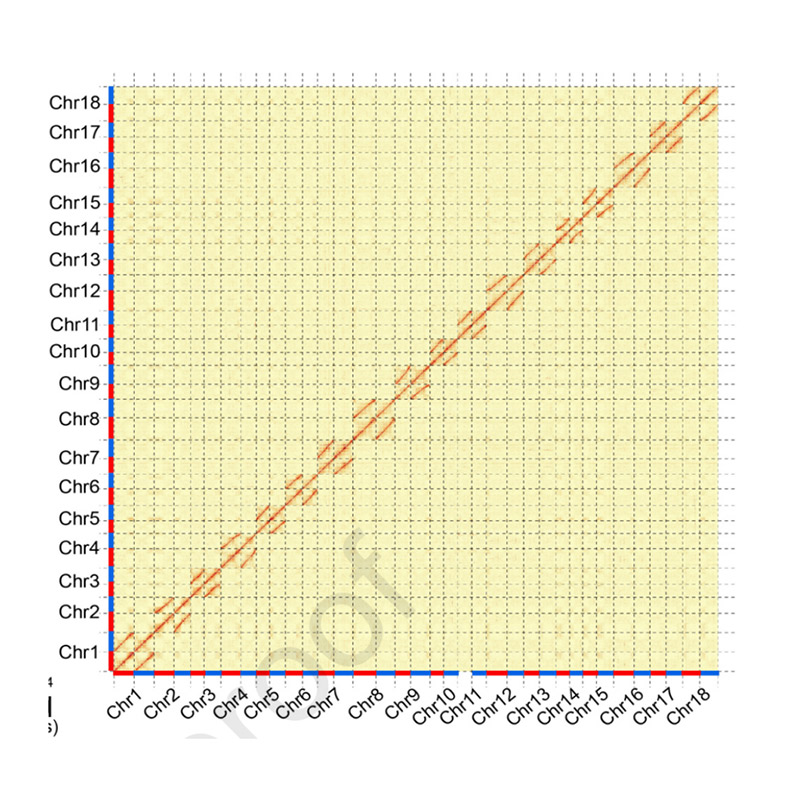
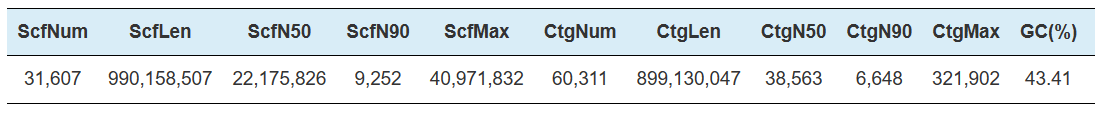
Hi-C Assembly – statistics
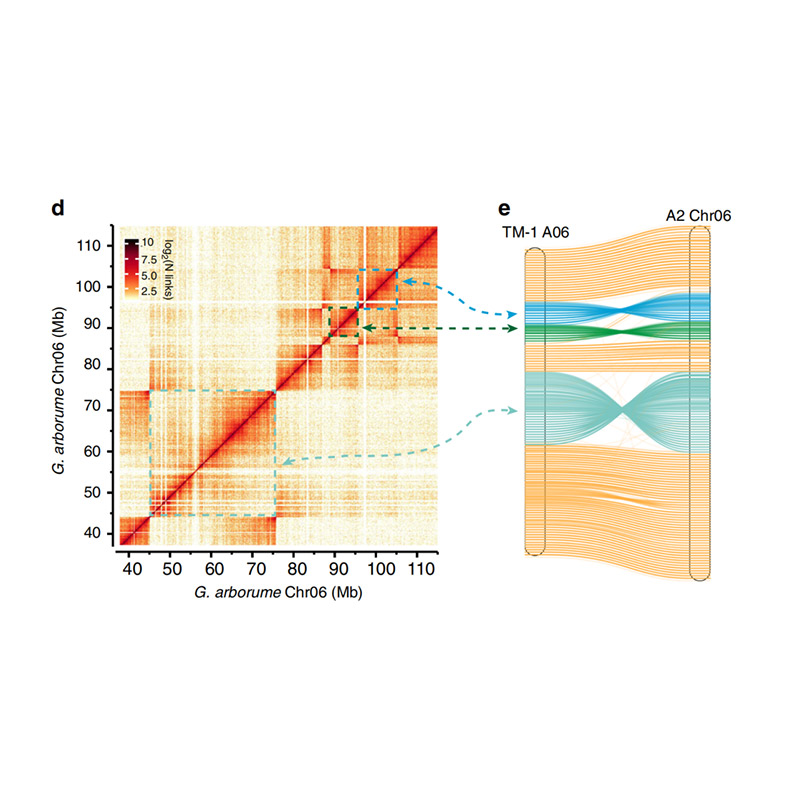
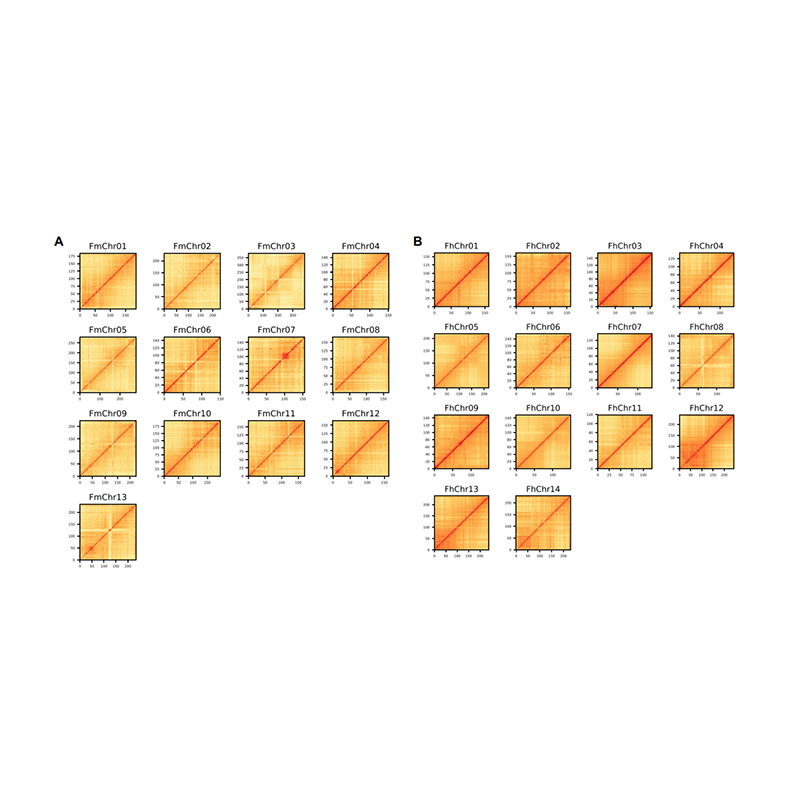
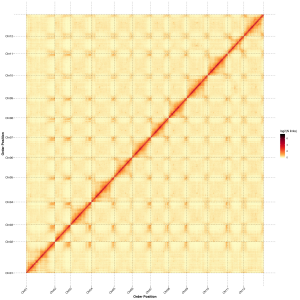
Post-assembly evaluation – heatmap of signal intensity between bins
Explore the advancements facilitated by BMKGene’s Hi-C assembly services through a curated collection of publications.
Tian, T. et al. (2023) ‘Genome assembly and genetic dissection of a prominent drought-resistant maize germplasm’, Nature Genetics 2023 55:3, 55(3), pp. 496–506. doi: 10.1038/s41588-023-01297-y.
Wang, Z. L. et al. (2020) ‘A Chromosome-Scale Assembly of the Asian Honeybee Apis cerana Genome’, Frontiers in Genetics, 11, p. 524140. doi: 10.3389/FGENE.2020.00279/BIBTEX.
Zhang, F. et al. (2023) ‘Revealing evolution of tropane alkaloid biosynthesis by analyzing two genomes in the Solanaceae family’, Nature Communications 2023 14:1, 14(1), pp. 1–18. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37133-4.
Zhang, X. et al. (2020) ‘Genomes of the Banyan Tree and Pollinator Wasp Provide Insights into Fig-Wasp Coevolution’, Cell, 183(4), pp. 875-889.e17. doi: 10.1016/J.CELL.2020.09.043