-

BMKMANU S3000_Spatial Transcriptome
Spatial transcriptomics stands at the forefront of scientific innovation, empowering researchers to delve into intricate gene expression patterns within tissues while preserving their spatial context. Amidst various platforms, BMKGene has developed the BMKManu S3000 Spatial Transcriptome Chip, boasting an enhanced resolution of 3.5µm, reaching the subcellular range, and enabling multi-level resolution settings. The S3000 chip, featuring approximately 4 million spots, employs microwells layered with beads loaded with spatially barcoded capture probes. A cDNA library, enriched with spatial barcodes, is prepared from the S3000 chip and subsequently sequenced on the Illumina NovaSeq platform. The combination of spatially barcoded samples and UMIs ensures the accuracy and specificity of the data generated. The BMKManu S3000 chip’s is extremely versatile, offering multi-level resolution settings that can be finely tuned to different tissues and desired levels of detail. This adaptability positions the chip as an outstanding choice for diverse spatial transcriptomics studies, ensuring precise spatial clustering with minimal noise. The use of cell segmentation technology with BMKManu S3000 enables the delimitation of transcriptional data to the boundaries of cells, resulting in an analysis that has direct biological meaning. Furthermore, the improved resolution of S3000 results in higher number of genes and UMIs detected per cell, enabling a much more accurate analysis of the spatial transcription patterns and clustering of cells.
-

DNBSEQ pre-made libraries
DNBSEQ, developed by MGI, is an innovative NGS technology that has managed to decrease further down the sequencing costs and increase throughput. Preparation of DNBSEQ libraries involves DNA fragmentation, preparation of ssDNA, and rolling circle amplification to obtain the DNA nanoballs (DNB). These are then loaded onto a solid surface and subsequently sequenced by combinatorial Probe-Anchor Synthesis (cPAS). DNBSEQ technology combines the advantages of having a low amplification error rate with using high density error patterns with nanoballs, resulting in sequencing with higher throughput and accuracy.
Our pre-made library sequencing service enables customers to prepare Illumina sequencing libraries from diverse sources (mRNA, whole genome, amplicon, 10x libraries, among others), which are converted to MGI libraries in our laboratories to be sequenced in DNBSEQ-T7, enabling high data amounts at lower costs.
-
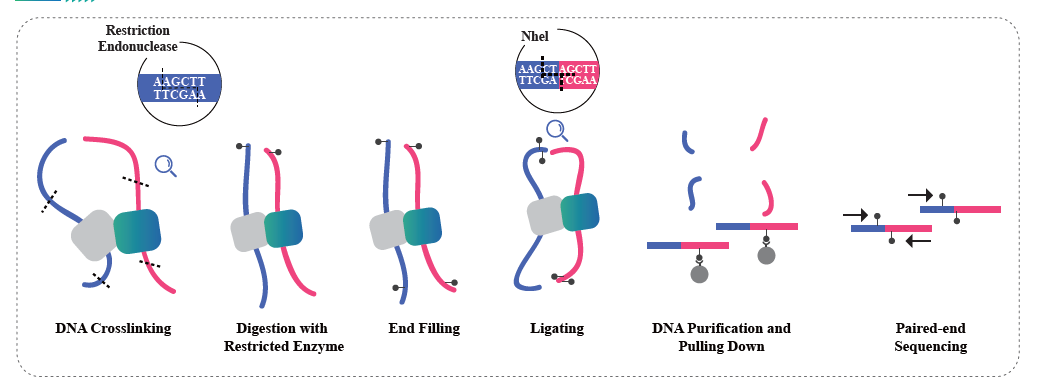
Hi-C based Chromatin Interaction
Hi-C is a method designed to capture genomic configuration by combining probing proximity-based interactions and high-throughput sequencing. The method is based on chromatin crosslinking with formaldehyde, followed by digestion and re-ligation in a way that only fragments that are covalently linked will form ligation products. By sequencing these ligation products, it is possible to study the 3D organization of the genome. Hi-C enables studying the distribution of the portions of the genome that are lightly packed (A compartments, euchromatin) and more likely to be transcriptionally active, and the regions that are more tightly packed (B compartments, Heterochromatin). Hi-C can also be used to pinpoint Topologically Associated Domains (TADs), regions of the genome that have folded structures and are likely to have similar expression patterns, and to identify chromatin loops, DNA regions that are anchored together by proteins and that are often enriched in regulatory elements. BMKGene’s Hi-C sequencing service empowers researchers to explore the spatial dimensions of genomics, opening new avenues for understanding genome regulation and its implications in health and disease.
-

TGuide Smart Viral DNA/RNA Kit
TGuide Smart Viral DNA/RNA Kit
The prefilled cartridge / plate reagent kit for purification viral DNA/RNA from blood, tissue, serum, plasma, body fluid, swab, tissue and sputum, etc.
-
TGuide Smart Magnetic Plant RNA Kit
TGuide Smart Magnetic Plant RNA Kit
Purify high-quality total RNA from plant tissues
-
TGuide Smart Blood/Cell/Tissue RNA Kit
TGuide Smart Blood/Cell/Tissue RNA Kit
The prefilled cartridge / plate reagent kit for purification of high-yield, high-purity, high-quality, inhibitor-free total RNA from animal tissue/cell/fresh whole blood
-
TGuide Smart Magnetic Plant DNA Kit
TGuide Smart Magnetic Plant DNA Kit
Purify high-quality genomic DNA from various plant tissues
-
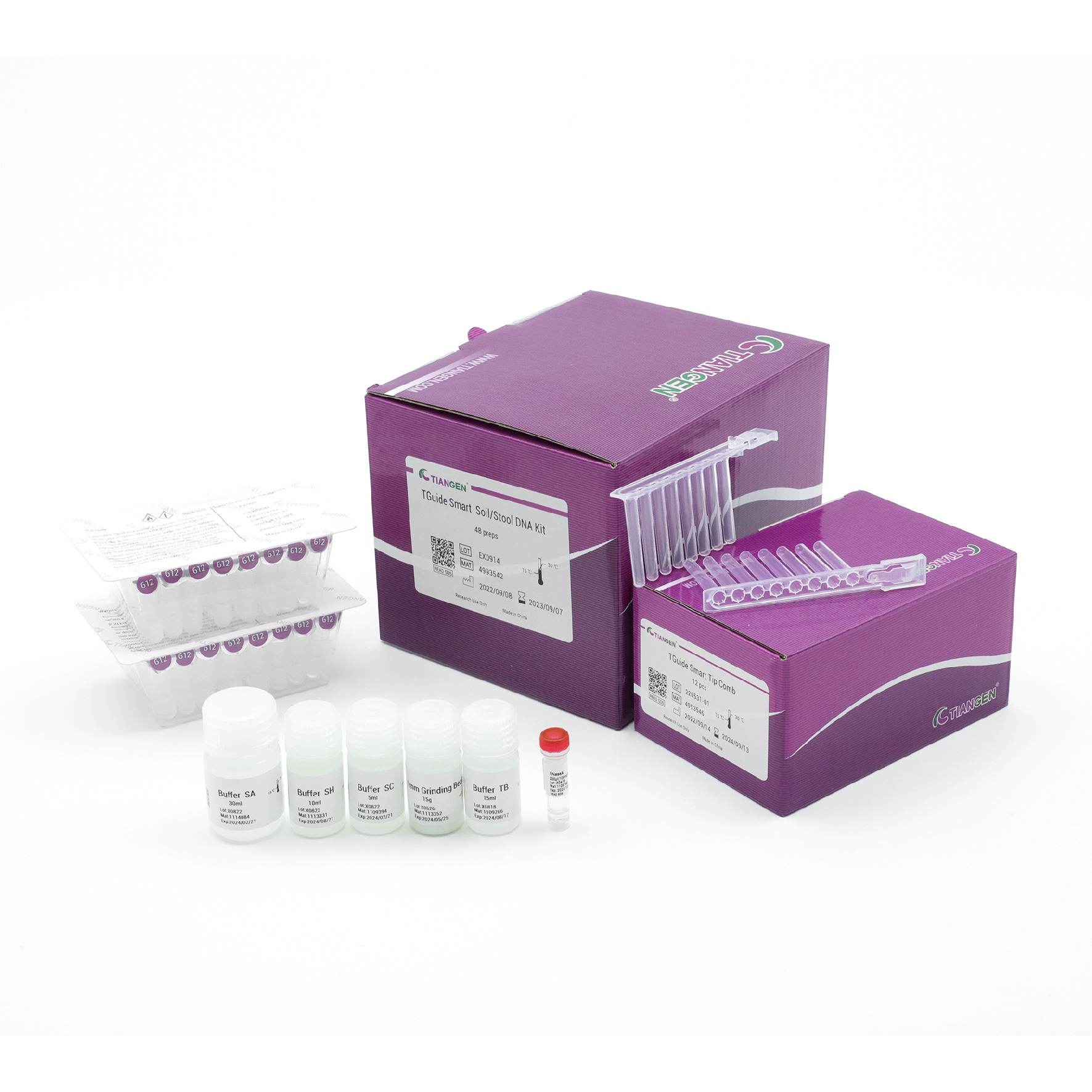
TGuide Smart Soil / Stool DNA Kit
TGuide Smart Soil / Stool DNA Kit
Purifies inhibitor-free DNA of high purity and quality from soil and stool samples
-
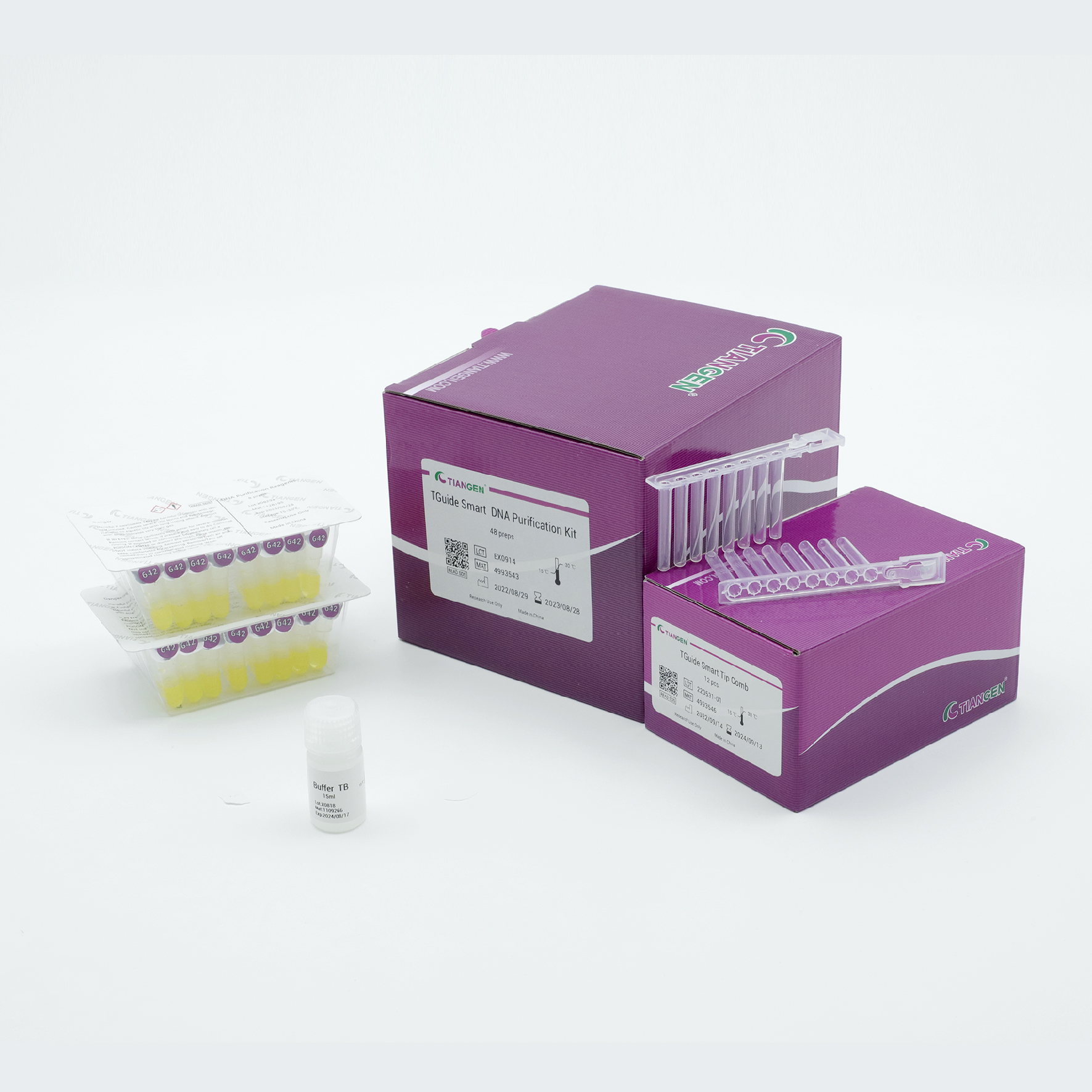
TGuide Smart DNA Purification Kit
Recovers high-quality DNA from PCR product or agarose gels.
-
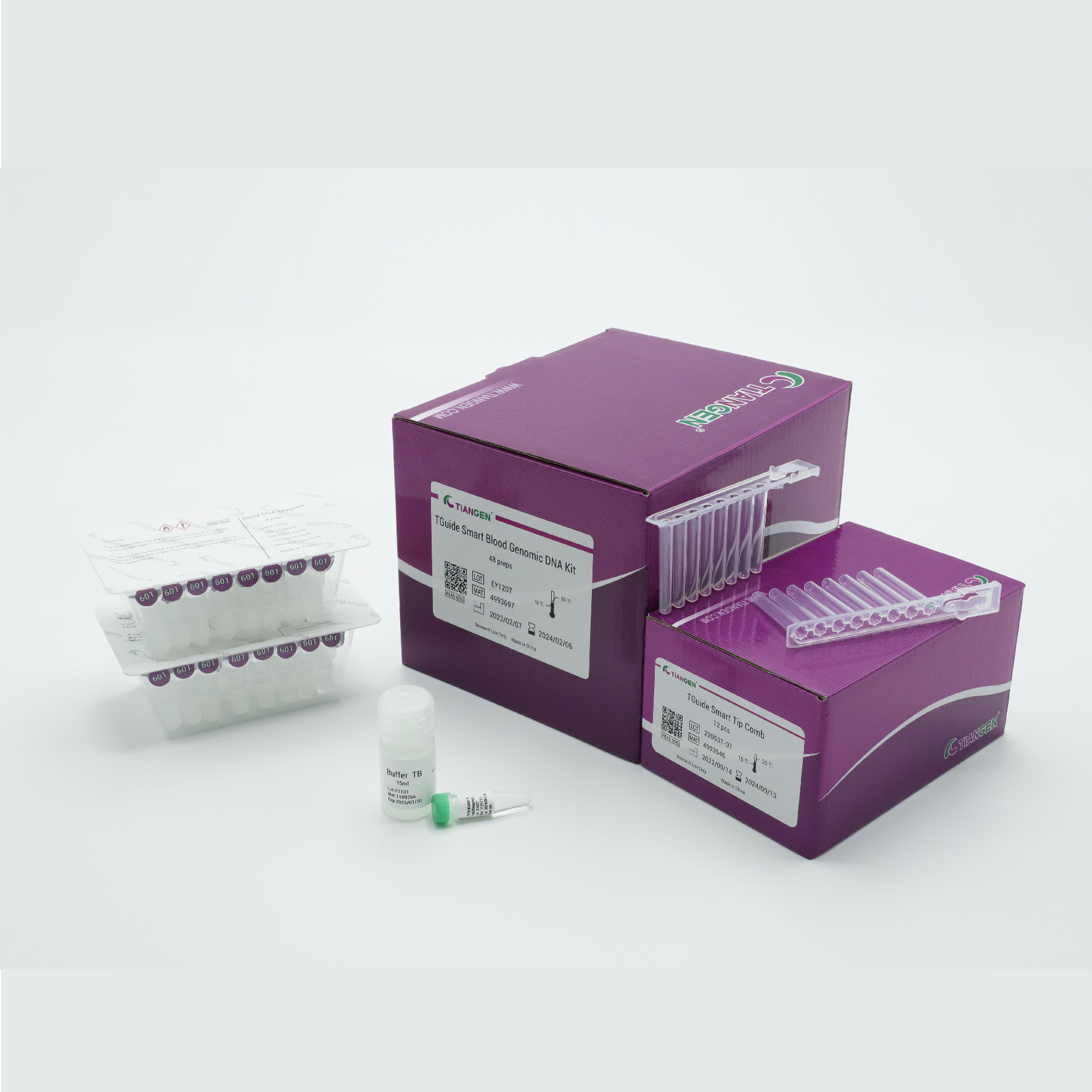
TGuide Smart Blood Genomic DNA Kit
TGuide Smart Blood Genomic DNA Kit
The prefilled cartridge / plate reagent kit for genomic DNA purification from blood and buffy coat
-
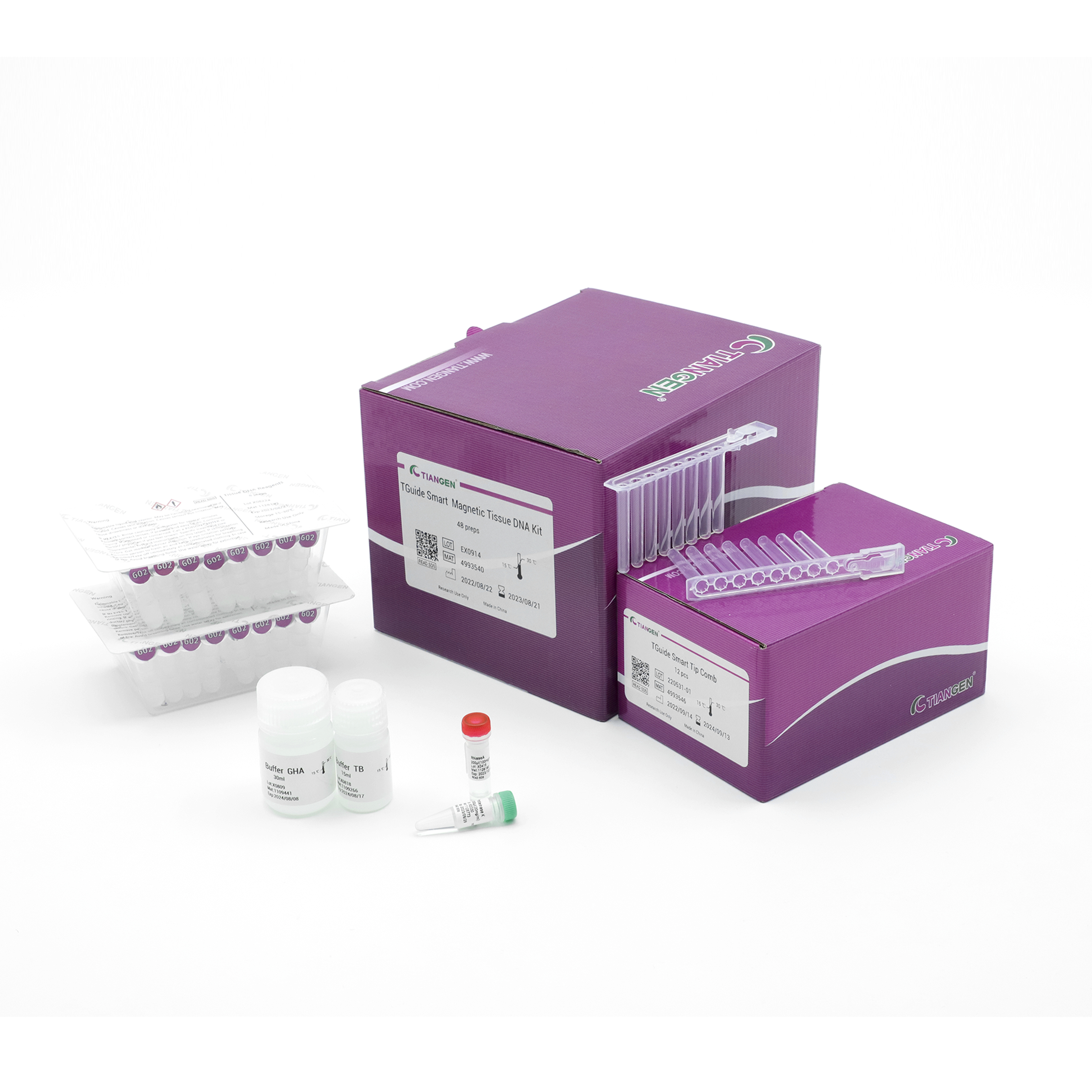
TGuide Smart Magnetic Tissue DNA Kit
The prefilled cartridge / plate reagent kit for genomic DNA extraction from animal tissues
-
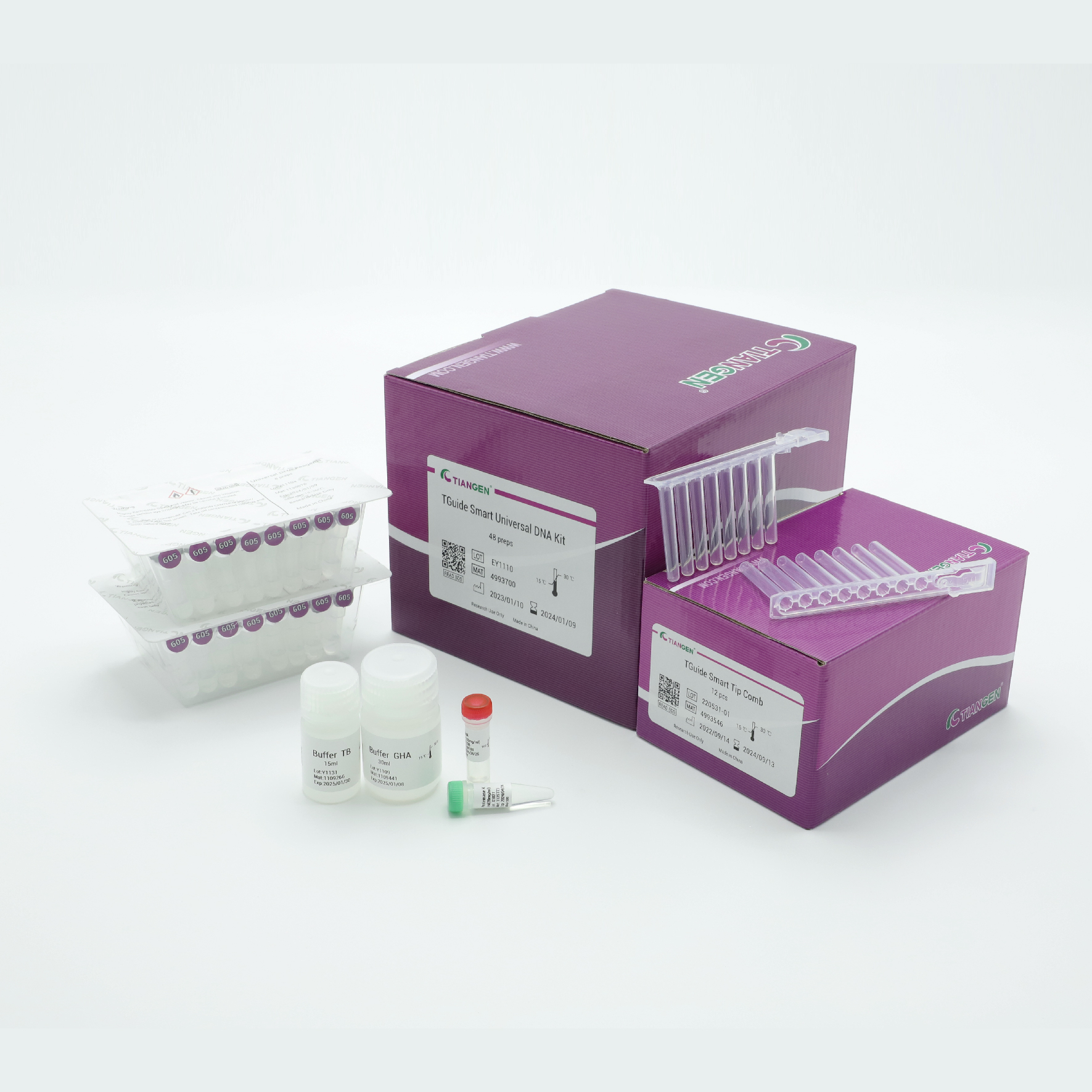
TGuide Smart Universal DNA Kit
The prefilled cartridge / plate reagent kit for purification genomic DNA from blood, dried blood spot, bacteria, cells, saliva, oral swabs, animal tissues, etc.
-

TGuide S16 Nucleic Acid Extractor
TGuide S16 Nucleic Acid Extractor
Easy-to-use Benchtop Instrument, 1-8 Or 16 Samples At The Same Time
Catalog number / packaging
Cat. no
ID
No. of preps
OSE-S16-AM
1 set

